Radiometric dating is used to estimate the age of rocks and other objects based on the fixed decay rate of radioactive isotopes. Learn about half-life and how it is used in different dating methods, such as uranium-lead dating and radiocarbon dating, in this video lesson.
Table of contents
Carbon is continually being created in the atmosphere due to the action of cosmic rays on nitrogen in the air. Carbon combines with oxygen to create carbon dioxide. Because plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis, this isotope ends up inside the plant, and because animals eat plants, they get some as well. When a plant or an animal dies, it stops taking in carbon The existing carbon within the organism starts to decay back into nitrogen, and this starts our clock for radiocarbon dating. A scientist can take a sample of an organic material when it is discovered and evaluate the proportion of carbon left in the relic to determine its age.
Radiometric dating is a method used to date rocks and other objects based on the known decay rate of radioactive isotopes. The decay rate is referring to radioactive decay , which is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by releasing radiation. Each radioactive isotope decays at its own fixed rate, which is expressed in terms of its half-life or, in other words, the time required for a quantity to fall to half of its starting value. There are different methods of radiometric dating.
Uranium-lead dating can be used to find the age of a uranium-containing mineral. Uranium decays to lead, and uranium decays to lead The two uranium isotopes decay at different rates, and this helps make uranium-lead dating one of the most reliable methods because it provides a built-in cross-check.
How do we determine the age of a rock?
Additional methods of radiometric dating, such as potassium-argon dating and rubidium-strontium dating , exist based on the decay of those isotopes. Radiocarbon dating is a method used to determine the age of organic material by measuring the radioactivity of its carbon content. With radiocarbon dating, we see that carbon decays to nitrogen and has a half-life of 5, years. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study. Did you know… We have over college courses that prepare you to earn credit by exam that is accepted by over 1, colleges and universities.
Radiometric Dating
You can test out of the first two years of college and save thousands off your degree. Anyone can earn credit-by-exam regardless of age or education level. To learn more, visit our Earning Credit Page. Not sure what college you want to attend yet? The videos on Study. Students in online learning conditions performed better than those receiving face-to-face instruction. Explore over 4, video courses. Find a degree that fits your goals.
- Radiometric dating.
- Radiometric Dating: Methods, Uses & the Significance of Half-Life.
- zim dating club.
- list of vietnam dating sites.
- dating 6 months and no i love you.
- dating sites for people with std.
- speed dating in wales sheep.
Learn about half-life and how it is used in different dating methods, such as uranium-lead dating and radiocarbon dating, in this video lesson. Try it risk-free for 30 days. An error occurred trying to load this video. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. Register to view this lesson Are you a student or a teacher? I am a student I am a teacher. What teachers are saying about Study. Conditions of Fossil Preservation: Are you still watching? Your next lesson will play in 10 seconds.
Radiometric Dating
Add to Add to Add to. Want to watch this again later? What is Radioactive Dating? Principles of Radiometric Dating. Relative Dating with Fossils: Index Fossils as Indicators of Time.
Radiometric Dating
Methods of Geological Dating: Numerical and Relative Dating. What is Relative Dating?
- UCSB Science Line;
- online dating voor studenten.
- glasgow internet dating.
- Principles of Radiometric Dating!
- free dating site pune.
- Dating Methods Using Radioactive Isotopes;
- Radioactive Dating | BioNinja;
What is the Age of the Solar System? Absolute Time in Geology. What is Carbon Dating? Methods for Determining Past Climates. Introduction to Physical Geology: Intro to Natural Sciences. Any material which is composed of carbon may be dated. Herein lies the true advantage of the radiocarbon method. Potassium-Argon K-Ar dating is the most widely applied technique of radiometric dating. Potassium is a component in many common minerals and can be used to determine the ages of igneous and metamorphic rocks. The Potassium-Argon dating method is the measurement of the accumulation of Argon in a mineral.
It is based on the occurrence of a small fixed amount of the radioisotope 40 K in natural potassium that decays to the stable Argon isotope 40 Ar with a half-life of about 1, million years. In contrast to a method such as Radiocarbon dating, which measures the disappearance of a substance, K-Ar dating measures the accumulation of Argon in a substance from the decomposition of potassium.
Argon, being an inert gas, usually does not leech out of a mineral and is easy to measure in small samples. This method dates the formation or time of crystallisation of the mineral that is being dated; it does not tell when the elements themselves were formed. It is best used with rocks that contain minerals that crystallised over a very short period, possibly at the same time the rock was formed. This method should also be applied only to minerals that remained in a closed system with no loss or gain of the parent or daughter isotope.
Uranium-Lead U-Pb dating is the most reliable method for dating Quaternary sedimentary carbonate and silica, and fossils particulary outside the range of radiocarbon. Quaternary geology provides a record of climate change and geologically recent changes in environment. U-Pb geochronology of zircon , baddelyite , and monazite is used for determining the age of emplacement of igneous rocks of all compositions, ranging in age from Tertiary to Early Archean.
U-Pb ages of metamorphic minerals, such as zircon or monazite are used to date thermal events, including terrestrial meteoritic impacts.
U-Pb ages of zircon in sediments are used to determine the provenance of the sediments. The Fission track analysis is based on radiation damage tracks due to the spontaneous fission of U. Fission-tracks are preserved in minerals that contain small amounts of uranium, such as apatite and zircon.
- You must create an account to continue watching!
- Navigation menu!
- !
Fission-track analysis is useful in determining the thermal history of a sample or region. By determining the number of tracks present on a polished surface of a grain and the amount of uranium present in the grain, it is possible to calculate how long it took to produce the number of tracks preserved. As long as the mineral has remained cool, near the earth surface, the tracks will accumulate. The oldest crystals on Earth that were formed on Earth are zircon crystals, and are approximately 4. Asteroids in the solar system have been clocked at 4.
We assume that the Earth is probably as old as the asteroids, because we believe the solar system to have formed from a collapsing nebula, and that the Earth, being geologically active, has simply destroyed any older zircon crystals that would be its true age, but we can't really be certain. The building blocks that the Earth is made of, the asteroids are 4. Based on astronomical models of how stars work, we also believe the Sun to be about 4. Radiometric dating is a widely accepted technique that measures the rate of decay of naturally occurring elements that have been incorporated into rocks and fossils.
Every element is defined by the particular number of protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up it's atoms. Sometimes, the number of neutrons within the atom is off. These atoms, with an odd number of neutrons, are called isotopes. Because they do not have the ideal number of neutrons, the isotopes are unstable and over time they will convert into more stable atoms. Scientists can measure the ratio of the parent isotopes compared to the converted isotopes. The rate of isotope decay is very consistent, and is not effected by environmental changes like heat, temperature, and pressure.
This makes radiometric dating quite reliable. However, there are some factors that must be accounted for. For example, sometimes it is possible for a small amount of new "parent" isotopes to be incorporated into the object, skewing the ratio. This is understood and can be corrected for. Carbon is the most commonly used isotope for dating organic material plants, animals. Plants and animals continually take in carbon during their lifespan. When they die, they no longer acquire carbon and so we can measure the decay of the isotope to determine when the plant or animal died. Because carbon decays relatively rapidly compared to other isotopes, it can only be used to date things that are less than 60, years old.
Anything older would have so little carbon left that you couldn't accurately measure it.
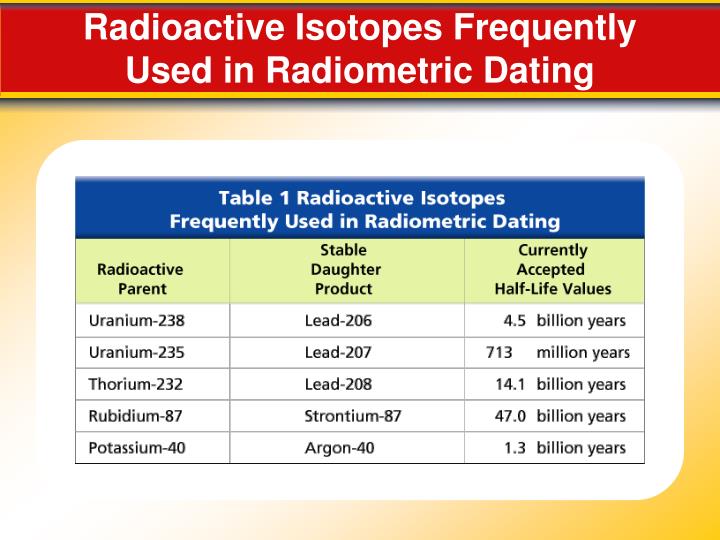
However, the rapid decay allows precise dating - accuracy within just a couple decades. When dating older objects, namely rocks, it is necessary to use other isotopes that take a much longer time to decay. The most common isotopes used are uranium and uranium there are multiple isotopes of uranium.
The uranium isotopes eventually convert into lead isotopes.