In radioactive decay, an element breaks down into be possible to measure the age of Earth by determining the.
Table of contents
- Non-Radiometric Dating of the Age of the Earth: Implications From Fossil Coral Evidence
- Age of the Earth
- Navigation menu
- Age of the Earth - Wikipedia
What is an earthquake? What is the highest magnitude an earthquake can reach?
- Radioactive Dating?
- taking it slow while dating.
- dating online free best sites.
- How is Earth's Age Calculated??
- south wales echo dating.
- southbank speed dating.
What are the biggest historical earthquakes? Why do earthquakes happen in clusters? Where are earthquakes expected in the world, especially in Asia? What is a supercontinent? Are all the faults on Earth active?
Non-Radiometric Dating of the Age of the Earth: Implications From Fossil Coral Evidence
How can human activities cause climate change? Why do urbanisation and deforestation make flooding more likely? Earthquake Hazards Is Singapore threatened by earthquakes? Can we predict earthquakes? Why does a building on solid bedrock resist better to an earthquake than a building on sediment or reclaimed land? Why does a building with base isolation resist better to an earthquake than a building without base isolation?
Why does a building with full bracing resist better to an earthquake than a building with no bracing? Impacts of Volcanic Hazards What are the principal signals of a volcanic unrest? How can we forecast volcanic eruptions? Tsunamis Where is a tsunami most likely to happen? Can Singapore be affected by a tsunami?
Can animals sense an impending tsunami? What should we do during a tsunami? Why do trees seem to resist more to tsunamis than houses? Why does a boat at sea experience a tsunami differently from a boat near the shore? Volcanoes All About Volcanoes What is the difference between magma and lava? Is lava always liquid? What does a magma chamber look like?
What are the largest eruptions in the world? Are earthquakes and volcanic eruptions related? Where can we find volcanoes on earth? Miscellaneous Miscellaneous Why are there mass extinctions? How did life appear on earth? How does photosynthesis work? This suggested that it might be possible to measure the age of Earth by determining the relative proportions of radioactive materials in geological samples.
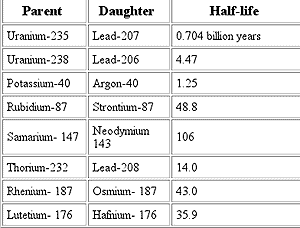
In reality, radioactive elements do not always decay into nonradioactive "stable" elements directly, instead, decaying into other radioactive elements that have their own half-lives and so on, until they reach a stable element. These " decay chains ", such as the uranium-radium and thorium series, were known within a few years of the discovery of radioactivity and provided a basis for constructing techniques of radiometric dating.
The pioneers of radioactivity were chemist Bertram B. Boltwood and the energetic Rutherford. Boltwood had conducted studies of radioactive materials as a consultant, and when Rutherford lectured at Yale in , [28] Boltwood was inspired to describe the relationships between elements in various decay series.
Late in , Rutherford took the first step toward radiometric dating by suggesting that the alpha particles released by radioactive decay could be trapped in a rocky material as helium atoms. At the time, Rutherford was only guessing at the relationship between alpha particles and helium atoms, but he would prove the connection four years later. Soddy and Sir William Ramsay had just determined the rate at which radium produces alpha particles, and Rutherford proposed that he could determine the age of a rock sample by measuring its concentration of helium.
He dated a rock in his possession to an age of 40 million years by this technique. I came into the room, which was half dark, and presently spotted Lord Kelvin in the audience and realized that I was in trouble at the last part of my speech dealing with the age of the Earth, where my views conflicted with his.
To my relief, Kelvin fell fast asleep, but as I came to the important point, I saw the old bird sit up, open an eye, and cock a baleful glance at me! Then a sudden inspiration came, and I said, "Lord Kelvin had limited the age of the Earth, provided no new source was discovered. That prophetic utterance refers to what we are now considering tonight, radium! Rutherford assumed that the rate of decay of radium as determined by Ramsay and Soddy was accurate, and that helium did not escape from the sample over time. Rutherford's scheme was inaccurate, but it was a useful first step.
Boltwood focused on the end products of decay series. In , he suggested that lead was the final stable product of the decay of radium. It was already known that radium was an intermediate product of the decay of uranium. Rutherford joined in, outlining a decay process in which radium emitted five alpha particles through various intermediate products to end up with lead, and speculated that the radium-lead decay chain could be used to date rock samples. Boltwood did the legwork, and by the end of had provided dates for 26 separate rock samples, ranging from 92 to million years.
He did not publish these results, which was fortunate because they were flawed by measurement errors and poor estimates of the half-life of radium. Boltwood refined his work and finally published the results in Boltwood's paper pointed out that samples taken from comparable layers of strata had similar lead-to-uranium ratios, and that samples from older layers had a higher proportion of lead, except where there was evidence that lead had leached out of the sample. His studies were flawed by the fact that the decay series of thorium was not understood, which led to incorrect results for samples that contained both uranium and thorium.
However, his calculations were far more accurate than any that had been performed to that time. Refinements in the technique would later give ages for Boltwood's 26 samples of million to 2. Although Boltwood published his paper in a prominent geological journal, the geological community had little interest in radioactivity.
Age of the Earth
Rutherford remained mildly curious about the issue of the age of Earth but did little work on it. Robert Strutt tinkered with Rutherford's helium method until and then ceased. However, Strutt's student Arthur Holmes became interested in radiometric dating and continued to work on it after everyone else had given up. Holmes focused on lead dating, because he regarded the helium method as unpromising. He performed measurements on rock samples and concluded in that the oldest a sample from Ceylon was about 1. For example, he assumed that the samples had contained only uranium and no lead when they were formed.
More important research was published in It showed that elements generally exist in multiple variants with different masses, or " isotopes ". In the s, isotopes would be shown to have nuclei with differing numbers of the neutral particles known as " neutrons ".
In that same year, other research was published establishing the rules for radioactive decay, allowing more precise identification of decay series. Many geologists felt these new discoveries made radiometric dating so complicated as to be worthless. His work was generally ignored until the s, though in Joseph Barrell , a professor of geology at Yale, redrew geological history as it was understood at the time to conform to Holmes's findings in radiometric dating.
Barrell's research determined that the layers of strata had not all been laid down at the same rate, and so current rates of geological change could not be used to provide accurate timelines of the history of Earth. Holmes' persistence finally began to pay off in , when the speakers at the yearly meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science came to a rough consensus that Earth was a few billion years old, and that radiometric dating was credible. Holmes published The Age of the Earth, an Introduction to Geological Ideas in in which he presented a range of 1.
No great push to embrace radiometric dating followed, however, and the die-hards in the geological community stubbornly resisted. They had never cared for attempts by physicists to intrude in their domain, and had successfully ignored them so far.
Navigation menu
Holmes, being one of the few people on Earth who was trained in radiometric dating techniques, was a committee member, and in fact wrote most of the final report. Thus, Arthur Holmes' report concluded that radioactive dating was the only reliable means of pinning down geological time scales. Questions of bias were deflected by the great and exacting detail of the report. It described the methods used, the care with which measurements were made, and their error bars and limitations.
Radiometric dating continues to be the predominant way scientists date geologic timescales. Techniques for radioactive dating have been tested and fine-tuned on an ongoing basis since the s. Forty or so different dating techniques have been utilized to date, working on a wide variety of materials. Dates for the same sample using these different techniques are in very close agreement on the age of the material.
Age of the Earth - Wikipedia
Possible contamination problems do exist, but they have been studied and dealt with by careful investigation, leading to sample preparation procedures being minimized to limit the chance of contamination. An age of 4. The quoted age of Earth is derived, in part, from the Canyon Diablo meteorite for several important reasons and is built upon a modern understanding of cosmochemistry built up over decades of research.